Optimism from earnings growth among large stocks overshadows concerns about instability abroad, quarterly debt sales, and the diminishing likelihood of an immediate interest rate cut.
“The U.S. is doing pretty well,” Yardeni Research founder Ed Yardeni remarks, noting a shift from speculation about interest rates allows the market to focus on fundamentals. “Right now, the fundamentals are good for the economy. And, there's plenty of hype around about.”
Multiple rate cuts totaling nearly 125 basis points in the next year remain expected. This seems extreme unless there's a market crash, says Harley Bassman, inventor of the MOVE Index measuring bond market volatility. Bassman believes current pricing reflects a bimodal scenario, with an 85% chance rates remain stable and a 15% chance they drop to 1%. Combining these probabilities, the market arrives at the anticipated cuts by year-end.
Naturally, markets are cyclical, moving from one extreme to another. Despite the fundamentals being in order, a lack of broad participation is evident in the more significant number of declining stocks than advancing ones. This situation, resembling patterns seen during the late ‘90s infotech-and-telecom boom, is frequently an indicator of less resilient future returns.
Ryan Detrick of Carson Capital Management notes that February typically experiences less momentum than January, often due to reinvestment and bonus inflows. Data shows that when the S&P 500 recorded a 20% gain for the year, February tended to underperform, especially in the latter half of the month, which typically marked the weakest two-week period of the year.

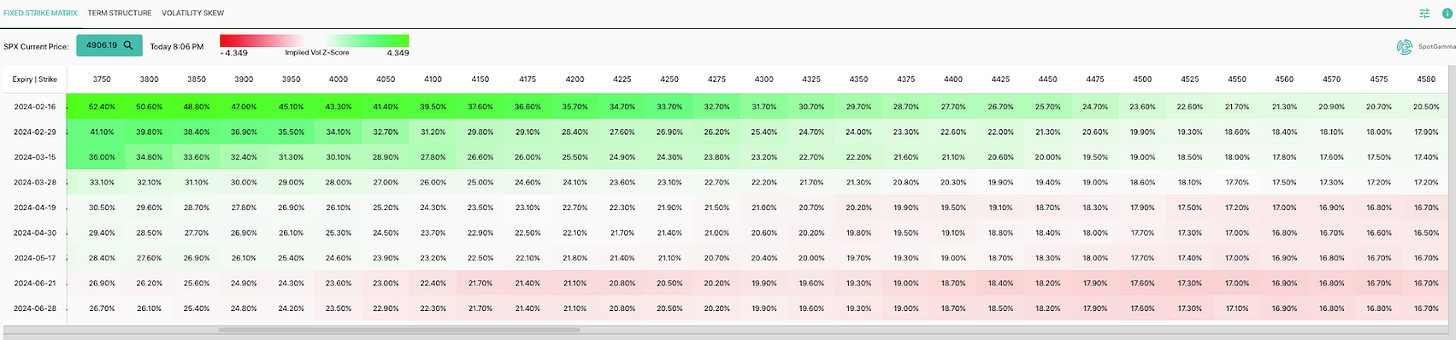
While the same volatility-suppressing trades detailed in last week’s letter continue to support markets where they are ceteris paribus (where customers sell volatility, and dealers hedge by buying stock/futures during declines and selling during strength), there has been “SPX/SPY downside buying (put flys) and ongoing VIX call buying,” Nomura Americas Cross-Asset Macro Strategist Charlie McElligott writes. This steepens implied volatility skew, benefitting the underappreciated hedge opportunities shared in Physik Invest’s Market Intelligence letters.
The recent repricing has allowed unbalanced, out-of-the-money options spreads to retain their value better amid ongoing market gains. The focus has shifted from worries about missed opportunities to safeguarding against potential downturns. This shift may be attributed to concerns beyond poor market breadth and the possibility of localized issues in places like China impacting global markets. These include geopolitical tensions, turbulence in specific capital market segments, lingering effects of extensive government spending, and looming debt crises.
With the popularity of yield-enhancing trades like selling options, there's concern that if significant market movements materialize, a greater share of end users will shift to buying options, indirectly exacerbating market volatility and downside.

To explain this phenomenon, we start with the options delta, which measures how much an option's price will change for every $1 change in the underlying asset's price. When end users sell put options, market makers buy them, assuming a negative delta stance, thus prompting them to acquire the underlying asset to hedge (which has a positive delta). Conversely, when end users buy put options, dealers sell them, taking on a positive delta. Consequently, they need to sell the underlying asset (which has a negative delta) to hedge. In sharp and volatile market declines, options sellers may opt to cover their positions by purchasing options, thereby diminishing stability as counterparties hedge in line with the market movement.
Kris Sidial from The Ambrus Group emphasizes second-order effects are further amplified due to the large scale of options selling, adding concentration among market makers as another risk to watch. Scott Rubner, a tactical specialist at Goldman Sachs Group, concurs current market problems, and the unwind of stretched positioning may lead to a weak February.







"Bassman believes current pricing reflects a bimodal scenario, with an 85% chance rates remain stable and a 15% chance they drop to 1%. Combining these probabilities, the market arrives at the anticipated cuts by year-end."
That's an interesting point of view.
"The focus has shifted from worries about missed opportunities to safeguarding against potential downturns."
The current relative extreme positions on the eminisp500 by the main actors could also favor a market correction. The concrete trigger could start from an increase in spreads on corporate bonds (I'll have to explain why). IMVHO