US consumer prices rose by 4.9% in the 12 months to April, down from the previous month's 5%. Wednesday’s figures suggest inflation is moderating and emboldens the case for a pause to interest rate increases.
“The Fed will want to see declines in these statistical measures for a few more months before it could feel comfortable about cutting rates,” John Authers writes.
Notwithstanding “sticky price inflation” falling (only “if shelter prices are excluded,” the most challenging “front in the battle on inflation”), applications to purchase and refinance homes rose with yields falling, and that’s exactly what the Fed doesn’t want.
Many maintain the Fed is looking to walk-up long-end yields, and that’s problematic for assets; higher interest rates portend lesser allocations toward risky assets.

Pimco’s Erin Browne and Emmanuel Sharef add that “12-month returns following the final rate hike could be flat for 10-year U.S. Treasuries, while the S&P 500 could sell off sharply.”

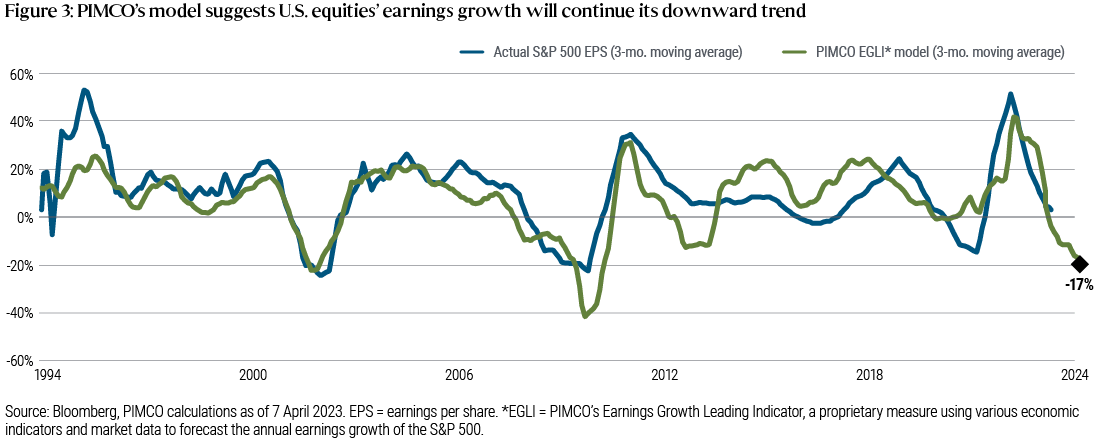
Accordingly, bonds look attractive “for their diversification, capital preservation, and upside opportunities,” while “earnings expectations appear too high, and valuations too rich,” warranting “underweight” equities positioning.
Compounding the risks are flows “that eventually will constrain lending and nominal growth on a 6- to 12-month horizon,” writes Goldman Sachs Group Inc (NYSE: GS).

In other news was worry over a US debt default.
The US government has been using accounting measures to provide cash after reaching a borrowing limit. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen informed Congress that these measures might be exhausted by June, resulting in payment disruptions; a default would cause an economic disaster and “global downturn,” threatening “US global economic leadership” and “national security,” Yellen says. A solution (e.g., to raise the debt ceiling) could manifest issuance of “a substantial amount of bills in 2H23 … that would drain liquidity,” Morgan Stanley (NYSE: MS) writes.
Despite the worry, markets are contained in part due to positioning contexts. Decline in realized volatility (RVOL), coupled with implied volatility (IVOL) premium, makes it difficult for the market to resolve directionally.
In fact, Nomura Holdings Inc (NYSE: NMR) said it sees “significant further potential for additional equities re-allocation buying from the vol control space over the next month if this ongoing rVol smash / tight daily ranges phenomenon holds—i.e., +$37.8B of US Equities to buy on theoretical 50bps daily SPX change).”

Options are sold systematically as traders aim to extract the premium; the Ambrus Group’s Kris Sidial says there is a puking off options exposures and short-bias activity (i.e., selling options) used as yield enhancement as traders call bluff on authorities not being there to prevent crises.

Should readers wish to hedge the debt ceiling debacle, June call options on the Cboe Volatility Index appear attractive, some suggest. But, with RVOL as low as it is, owning optionality is not generally warranted. The risk is lower volatility, not higher.
About
Welcome to the Daily Brief by Physik Invest, a soon-to-launch research, consulting, trading, and asset management solutions provider. Learn about our origin story here, and consider subscribing for daily updates on the critical contexts that could lend to future market movement.
Separately, please don’t use this free letter as advice; all content is for informational purposes, and derivatives carry a substantial risk of loss. At this time, Capelj and Physik Invest, non-professional advisors, will never solicit others for capital or collect fees and disbursements. Separately, you may view this letter’s content calendar at this link.





